![[internet geography]](../images/pagelayout/netgeologo.gif)
![]()
Physical Geography
Coasts
Earthquake
Ecosystems
Glaciation
Limestone
Plate Tectonics
Rivers
Volcanoes
Weather and climate
National Parks
Human Geography
Landuse
Migration
Urbanisation
Economic Geography

|
Earthquakes |
|
An earthquake is a sudden movement of the earth's surface. You can find out about current earthquakes here.
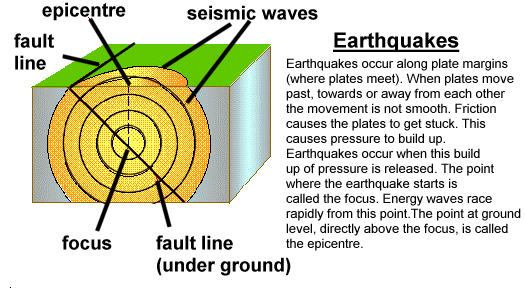
Earthquakes are caused by the movement of the earth's tectonic plates. Earthquakes occur where the earth's plates meet along plate boundaries (see plate tectonics page for more infomration on this).For example as two plates move towards each other, one can be pushed down under the other one into the mantle. If this plate gets stuck it causes a lot of pressure on surrounding rocks. When this pressure is released it produces shock waves. These are called seismic waves. This is an earthquake. The waves spread out from the point where the earthquake started - the focus. More damage is done near the focus. The point on the earth's surface directly above the focus is the epicentre.
The effects of earthquakes vary. This is a result of a variety of factors such as the strength of the earthquake, the level of population in an area and the level of economic development of the area struck.
The magnitude (size) of an earthquake is measured using a seismometer. This is a machine that measures movements in the earth's surface. The Richter Scale measures earthquakes on a logarithmic scale - this means that an earthquake of 6 is ten times more powerful than one with a score of 5.
At
05.46 on 17th January 1995 an earthquake measuring 7.2 on the
Richter scale struck the heavily populated city of Kobe,
Japan. The earthquake occurred along the destructive plate boundary
where the Pacific and the Philippine Plate (oceanic) meet the
Eurasian (continental) plate.
GeoNet
- What? Where? When? Why? So What? of the 1999 Turkish Earthquake
The
Turkish earthquake occurred on Tuesday 17th August 1999 at 3.02
a.m. local time (12 am GMT). The earthquake lasted 45 seconds
and measured 6.8 - 7.0 on the Richter Scale. See the BBC
News web site for detailed case study information and images
on the Turkish
Earthquake.
You
can download a factfile about the Turkish Earthquake
here.
California lies on the conservative margin where the Pacific Plate slides alongside the North American Plate (timeline of movement). As a result it is susceptible to earthquakes. The 1906 Earthquake almost destroyed San Francisco. Later, in 1989 an earthquake measuring 6.9 on the Richter Scale hit San Francisco. |
![]()
GeoNet is not responsible for the content of any of these sites
Earthquakes
- Past, present and future
Earthquakes - Why the earth shakes
Earthquake
Fact Sheet
(Downloadable
basic activity sheet about earthquakes 52kb Word 97 format)