![[internet geography]](../images/pagelayout/netgeologo.gif)
![]()
Physical Geography
Coasts
Earthquake
Ecosystems
Glaciation
Limestone
Plate Tectonics
Rivers
Volcanoes
Weather and climate
National Parks
Human Geography
Landuse
Migration
Urbanisation
Economic Geography

|
Plate Tectonics
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
When studying plate-tectonics the best starting point is examining the structure of the earth. The earth is very similar to a peach in its structure. In the centre is a solid core. Surrounding the core is the inner core, then the mantle, which is covered in the earths 'skin' or crust. Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
In
1912 Alfred
Wegener published a theory to explain why the Earth looked
like a huge jigsaw. He believed the continents were once joined
forming a supercontinent he called Pangaea.
Over 180 million years ago this supercontinent began to "break
up" due to continental drift.
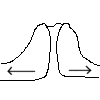
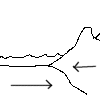
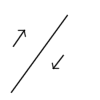
The point where two or more plates meet is known as a plate boundary. There are four main types of plate boundary. These are constructive, destructive, conservative and collision margins.
|