![[internet geography]](../images/pagelayout/netgeologo.gif)
![]()
Physical Geography
Coasts
Earthquake
Ecosystems
Glaciation
Limestone
Plate Tectonics
Rivers
Volcanoes
Weather and climate
National Parks
Human Geography
Landuse
Migration
Urbanisation
Economic Geography

|
Waves Waves
There
are four main processes which cause coastal erosion. These are
corrasion/abrasion, hydraulic action, attrition and corrosion/solution.
Corrasion/abrasion is when waves pick up beach material (e.g. pebbles) and hurl them at the base of a cliff. When waves hit the base of a cliff air is compressed into cracks. when the wave retreats the air rushes out of the gap. Often this causes cliff matrial to break away. This process is known as hydraulic action. Attrition is when waves cause rocks and pebbles to bump into each other and break up. Corrosion/solution is when certain types of cliff erode as a result of weak acids in the sea. Erosion is greatest when waves break at the foot of a cliff. This causes erosion at the base of the cliff. This creates a wave-cut notch in the base of the cliff. As the notch increases in size the weight of the cliffs above become too much and the cliff collapses. This material will provide temporary protection for the cliff behind. However, once it has been removed by the sea this process will occur again. Where cliffs are made of more resistant material, wave cut platforms will be created.
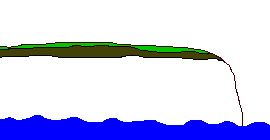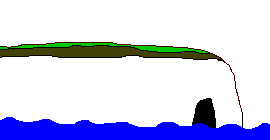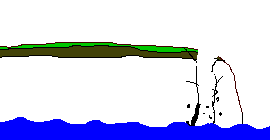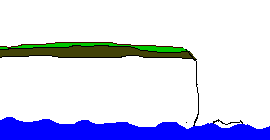
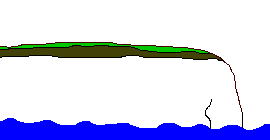
A
headland is an area of hard rock which sticks out into the sea.
Headlands form in areas of alternating hard and soft rock. Where
the soft rock erodes bays are formed either side of the headland.
As the headland becomes more exposed to the wind and waves the
rate of its erosion increases. When headlands erode they create
distinct features such as caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
The diagram below shows the sequence in the erosion of a headland.
|
![]()
GeoNet is not responsible for the content of any of these sites