![[internet geography]](../images/pagelayout/netgeologo.gif)
![]()
Physical Geography
Coasts
Earthquake
Ecosystems
Glaciation
Limestone
Plate Tectonics
Rivers
Volcanoes
Weather and climate
National Parks
Human Geography
Landuse
Migration
Urbanisation
Economic Geography

|
World Climate
|
|
|
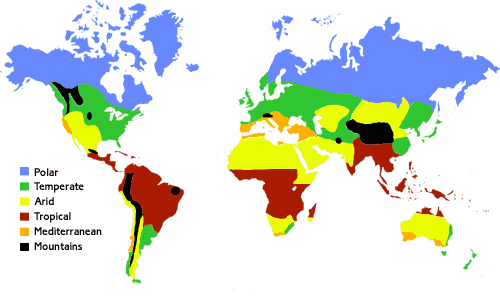
The world
has several climatic zones. These are summarised on the map below.
(Image
curtesy of the UK Meteorlogical Office)
The classification is based on maximum and minimum temperatures and the temperature range as well as the total and seasonal distribution of precipitation. Simple summary of climatic zones: Polar - very
cold and dry all year There are 5 factors which affect climate. These are summerised below: Latitude Tempature range increases with distance from the equatot. Also, temperatures decrease as you move away from the equator. This is because the suns rays are dispersed over a larger area of land as you move away from the equator. This is due to the curved surface of the earth. In addition polar regions are colder because the suns rays have further to travel compared to place on the equator. Altitude Temperatures decrease with height. The air is less dense and cannot hold heat as easily. Winds If winds are warm - they have been blown from a hot area - they will raise temperatures. If winds have been blown from cold areas they will lower temperatures. Distance from the sea (continentality) Land heats and cools faster than the sea. Therefore coastal areas have a lower temperature range than those areas inland. On the coast winters are mild and summers are cool. In inland areas temperatures are high in the summer and cold in the winter. Aspect Slopes facing the sun are warmer than those that are not. Thus south facing slopes in the northern hemisphere are usually warm whereas slopes facing north in the southern hemisphere are warmest. Climate can be displayed on a graph. A climate graph contians two pieces of information. The amount of rainfall and the temperature of an area. The temperature is shown as a line and the rainfall is displayed as bars. The figures are usually calculated as an avergae over a number of years. This reduces the impact of any anomolies in the weather affecting the statistics.
|
![]()
GeoNet is not responsible for the content of any of these sites
.